No products
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
There are 0 items in your cart. There is 1 item in your cart.
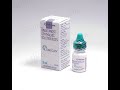
Lumigan
New
Lumigan contains bimatoprost as the main component. Bimatoprost is used to lower the increased intraocular pressure in adults. Lumigan is also can be used as a solution for eyelashes growth. When applied on the upper eyelid it significanly enhances growth phase of eyelashes making them thicker and darker.
288 Items
More info


LUMIGAN is an eyelash growth formula.
If Lumigan is used for eyelashes growth, the following method of administration is applied. If you use Lumigan for glaucoma treatment, consult your doctor for the recommended dosage.
|
Basic Information
|
 |
Are you still troubled by these problems?
Lumigan is a commercial name of Bimatoprost. Bimatoprost is also known under different trade names like Latisse, Bimat, Careprost, and many others.
Lumigan is initially was prescribed for glaucoma treatment, but accidentally was found to be effective in enhancement of lashes' growth. After that Allergan launched a new product Latisse focused only on lashes growth. However, both products Latisse and Lumigan are absolutely identical.
Lumigan helps to restore the normal growth cycle of lashes making them thicker, longer, and darker. It is the only product approved by the FDA and EU for hypotrichosis treatment, a condition characterized by inadequate lashes growth.

Activate Eyelashes Growth Power
Forget about artificial lashes. You can enjoy natural thick, long, and dark lashes again with Lumigan solution. Bimatoprost containing in Lumigan is the best eyelash formula available with clinically proven results in 8 weeks and fantastic results in just 16 weeks.
Insufficient, fragile, not curlings lashes are no longer a problem. Use the Lumigan solution and the results will surprise you. Keep in mind that Lumigan is a glaucoma medication. Do not apply Lumigan directly into the eyes if you use it for lashes growth. Lumigan is also not used for blepharitis and other eye infections that may affect lashes' growth. It affects only the growing cycle of eyelash follicles. 

|
Why do you need to use Lumigan solution? |
||||
|
 |
|||
|
How to Use Lumigan |
||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Ensure you don't wear contact lenses and your face is clean. It is recommended to use Lumigan solution before bedtime. | Use only a sterile applicator and hold it horizontally. Put only one drop of Lumigan solution on the applicator close to the tip. Do not use more than 1 drop because if used more, the solution may get into the eyes and cause pain and irritation. | Draw the applicator along the skin at the base of upper eyelashes starting from the inner part and going them to the outer part. | Remove any excess solution using a tissue or cotton. If not removed, the solution may cause hair growth in the area new the eyes. | Dispose of an applicator after each use. Repeat the procedure for opposite eyelids using a new sterile applicator. Do not apply to the lower eyelid. Do not touch the tip of the bottles with fingers and any surfaces as it may cause contamination of the solution. |
Lumigan weekly progress
The results may vary depending on many factors such as age, eyelashes condition, and many others. According to the results of clinical studies, first visible results are achieved within 8 weeks.
- 1st week – 5% growth (Lumigan). You just start your journey in lashes growth.
- 4th week – 15% growth. The results are still not pronounced. It is important to continue using Lumigan for lashes growth.
- 8th week – 50% growth of eyelashes with Lumigan. First good results are observed. Lashes become thicker, longer, and darker.
- 12th week – 69% growth with Lumigan. The lashes look gorgeous..
- 16th week – 78%-82% growth with Lumigan. Final results are achieved. The length of the lashes is almost doubled.
- 20th week – 82-106% growth with Lumigan. Stabilization of lashes length.
Full satisfaction is guaranteed!!!
Latisse and Lumigan are identical products made by the same manufacturer Allergan. Both products contain the same active ingredient Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03% 3ml, which is used for glaucoma treatment and lashes growth. Lumigan is the best solution for lashes growth.
- Latisse=Lumigan
- Same active ingredient - Bimatoprost
- Same composition
- Same volume
- Same results for less money
- Same manufacturer
- Identical products

Lumigan brief description
Product name - Lumigan - Bimatoprost ophtalmic solutiom 0.03% 3ml
Qualitative and quantitative composition - The primary compound is the bimatoprost. The concentration is 0.1 mg/ml bimatoprost. In effect, the solution contains 0.2 mg of benzalkonium chloride representing 0.1 mg bimatoprost.

Indication - Lumigan eye drop is indicated to decrease increased pressure in the eyes of people with open-angle or closed-angle glaucoma, as well as iridotomy or ocular hypertension. Lumigan is also widely used with cosmetic purpose to increase eyelashes growth.
Lumigan and Latisse are identical products in respect to composition, active and non-active ingredients, action mechanism and mode of administration.
Mode of administration - Simply have 1 drop of bimatoprost eye drops to each of your eyes or the affected every 24 or 12 hours (as directed by your physician), for a total of 1 or 2 drops per day. Usually, it is applied only once a day. If you need to use other drops, wait 5 minutes to place the other medicine.
If you use contact lenses, remove them before giving the eye drops and put them back in place after 15 minutes. This is because the eye drops can be absorbed by the lens and get damaged. Never touch the nozzle of the eye drop bottle to avoid contamination.
If you missed a dose, do not try to double the dose next time. You can take the missed dose if you still have considerable time left for the next dose. Usually, an overdose of Lumigan is not harmful but may reduce its effectiveness.
When Lumigan is used with purpose to increase eyelashes growth, it is applied 1 drops on the base of upper eyelid once daily before bedtime.
Contraindication - Lumigan eye drops should not be used if you are allergic to bimatoprost or any of the ingredients of this formulation. It is also not recommended for children or adolescents to use this medication because it is not known if it is safe at these ages.
It should not be used if you had some viral infections of the eye in the past such as herpes or eyeball and iris inflammation because they may possibly flare up again by this treatment. If you are having a slow pulse or low blood pressure, refrain from using it as the active ingredient can further lower it.
Special cautions and warnings - Lumigan should only be used during pregnancy or in lactating mothers if the ophthalmologist considers it necessary. As the safety and efficacy of bimatoprost in children and adolescents have not been studied, use in this age group is prohibited.
Lumigan can cause allergic reactions. Signs of this may include redness of the eyes and surrounding area, runny nose, itching, mucosal swelling, itching and redness of the eyes, shortness of breath (asthma). In rare cases, allergic shock syndrome may occur and the patient may get unconscious.
If you notice signs of an allergic reaction, inform a doctor immediately.
Drug interaction - If the active ingredient is used with other similar substances (such as latanoprost, travoprost) on the eye, the effect on intraocular pressure may get reduced. No further interactions are known. Still, do not use other eye medicines unless your doctor tells you to do so.
It is unlikely that other medications you take will have an effect on Lumigan, but if you are taking Ayurvedic or other types of natural medicines for which drug interactions are not known, it is better to stop using them simultaneously.
Side effects - Lumigan eye drops have common side effects, such as a slightly blurred vision shortly after the application of the medicine, which can affect driving. So avoid driving just after applying Lumigan. Other Lumigan side effects include redness of the eyes, eyelash growth and tingling of the eyes. Sensation such as dry eye, burning sensation in the eye, pain in the eye, blurred vision, inflammation of the cornea and eyelids can be seen.
Interesting facts
-
After opening, the eye drops are stable for four weeks only
-
Lumigan contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride that can discolor soft contact lenses
-
Some patients are sensitive to the preservative benzalkonium chloride
The charm of your eyes depends on your eyelashes
It is your turn to try Bimat and enjoy your natural eyelashes. Your wish comes true with Latisse generic.
We guarantee that you won't be disappointed. Just give a try!
100% Satisfaction Guarantee or Money Back!
Lumigan Real Shots

Full Original Product Annotation

Lumigan 0.03% 3ml FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
CONTENTS1. INDICATIONS
7. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 7.1 Pregnancy
- 7.2 Lactation
- 7.3 Pediatric Use
- 7.4 Geriatric Use
- 7.5 Renal Impairment
- 7.6 Hepatic Impairment
- 7.7 Compromised Respiratory Function
- 7.8 Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
8. OVERDOSAGE
9. DESCRIPTION
- 10.1 Mechanism of Action
- 10.2 Pharmacokinetics
13. HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
14. PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- 14.1 Potential for Pigmentation
- 14.2 Potential for Eyelash Changes
- 14.3 Handling the Container
- 14.4 When to Seek Physician Advice
- 14.5 Use with Contact Lenses
- 14.6 Use with Other Ophthalmic Drugs
* Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03% (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LUMIGAN™.
LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03% (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution)
INDICATIONS
LUMIGAN™ is a prostaglandin analog indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
One drop in the affected eye(s) once daily in the evening.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Solution containing 0.1 mg/mL bimatoprost (LUMIGAN™ 0.01%) or containing 0.3 mg/mL bimatoprost (LUMIGAN™ 0.03%). (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
LUMIGAN™ is contraindicated in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity to bimatoprost or to any of the excipients.
WARNINGSAND PRECAUTIONS
- Pigmentation of the iris, periorbital tissue (eyelid) and eyelashes can occur. Iris pigmentation is likely to be permanent. (5.1).
- Eyelash Changes
Gradual change to eyelashes including increased length, thickness and number of lashes. Usually reversible. (5.2).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported treatment-related adverse event was conjunctival hyperemia (mostly mild and thought to be of a non-inflammatory nature) occurring in 29% of patients with LUMIGAN 0.01 % and in 45% of patients with LUMIGAN 0.03 % (6.1).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Use in pediatric patients has not been evaluated and therefore use is not recommended in children and adolescents. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Lumigan FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1. INDICATIONSLUMIGAN™ 0.01 % and 0.03% (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Standard Adult Dosage
The recommended dosage is one drop in the affected eye(s) once daily in the evening. The dosage of LUMIGAN™ should not exceed once daily since it has been shown that more frequent administration may lessen the intraocular pressure lowering effect (See Section 5, Warnings and Precautions).
LUMIGAN™ may be used concomitantly with other topical ophthalmic drug products to lower intraocular pressure (See Section 5, Warnings and Precautions). If more than 1 topical ophthalmic medicinal product is being used, each one should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
3. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Sterile Ophthalmic solution containing bimatoprost 0.1 mg/mL (LUMIGAN™ 0.01%) or containing bimatoprost 0.3 mg/mL (LUMIGAN™ 0.03%).
4. CONTRAINDICATIONS
LUMIGAN™ is contraindicated in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity to bimatoprost or to any of the excipients.
5. WARNINGSAND PRECAUTIONS
LUMIGAN™ should be used with caution in patients with active intraocular inflammations (e.g. uveitis) because the inflammation may be exacerbated.
Macular edema, including cystoid macular edema, has been reported during treatment with LUMIGAN™ 0.03 % ophthalmic solution for elevated IOP.
LUMIGAN™ should be used with caution in aphakic patients, in pseudophakic patients with a torn posterior lens capsule, or in patients with known risk factors for macular edema (e.g. intraocular surgery, retinal vein occlusions, ocular inflammatory disease and diabetic retinopathy).
Increased iris pigmentation has occurred when bimatoprost solution has been administered.
Patients should be advised about the potential for increased brown iris pigmentation which is likely to be permanent. The pigmentation change is due to increased melanin content in the melanocytes rather than to an increase in the number of melanocytes. The long term effects of increased iridial pigmentation are not known. Iris color changes seen with ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost may not be noticeable for several months to years. Neither nevi nor freckles of the iris appear to be affected by treatment.
Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution has been reported to cause changes to pigmented tissues. When LUMIGAN™ 0.03 % was instilled directly into the eye (for treatment of elevated
(IOP), the most frequently reported pigmentary changes have been increased pigmentation of periorbital tissue (eyelid), eyelashes and the iris. Periorbital tissue pigmentation has been reported to be reversible in some patients.
There is the potential for hair growth to occur in areas where LUMIGAN™ solution comes repeatedly in contact with the skin surface. Thus, it is important to apply LUMIGAN™ as instructed and to avoid it running onto the cheek or other skin areas.
There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent ocular disease. Patients with a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface are at greater risk of developing bacterial keratitis.
Patients should be instructed to avoid allowing the tip of the dispensing container to contact the eye or surrounding structures to avoid eye injury and contamination of the solution.
LUMIGAN™ contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride, which may be absorbed by and cause discoloration of soft contact lenses. Patients wearing soft (hydrophilic) contact lenses should be instructed to remove contact lenses prior to administration of LUMIGAN™ and wait at least 15 minutes following administration before reinserting soft contact lenses.
Before treatment is initiated, patients should be informed of the possibility of eyelash growth since this has been observed during treatment with prostaglandin analogues, including LUMIGAN™.
LUMIGAN™ has not been studied in patients with inflammatory ocular conditions, vascular, inflammatory, angle-closure glaucoma, congenital glaucoma or narrowangle glaucoma.
In LUMIGAN™ 0.03% studies in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension, it has been shown that more frequent exposure of the eye to more than one dose of bimatoprost daily may decrease the IOP-lowering effect. Patients using LUMIGAN™ with other prostaglandin analogs should be monitored for changes to their intraocular pressure.
No drug interaction studies have been performed.
No interactions are anticipated in humans, since systemic concentrations of bimatoprost are extremely low (less than 0.2 ng/mL) following ocular dosing with LUMIGAN™ 0.03% eye drops. Bimatoprost is biotransformed by any of multiple enzymes and pathways, and no effects on hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes were observed in preclinical studies in rats and monkeys.
In clinical studies, LUMIGAN™ 0.03% eye drops (multidose) was used concomitantly with a number of different ophthalmic beta-blocking agents without evidence of interactions. Concomitant use of LUMIGAN™ and anti-glaucomatous agents other than topical beta blockers has not been evaluated during adjunctive glaucoma therapy.
There is a potential for the IOP-lowering effect of prostaglandin analogs (e.g., LUMIGAN™) to be reduced in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension when used with other prostaglandin analogs.
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
LUMIGAN™ 0.01%
In a 12-month, Phase 3 clinical study, in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension, approximately 38% (71/185) patients treated with LUMIGAN™ 0.01% eye drops solution experienced undesirable effects considered related to treatment. The most frequently reported treatment-related adverse event was conjunctival hyperemia (mostly mild and thought to be of a non-inflammatory nature) occurring in 29% of patients. Approximately 4% (8/185) of patients in the LUMIGAN™ 0.01% arm of the study discontinued due to any adverse event in the 12-month study, with 1.6% (3/185) discontinuing due to conjunctival hyperemia. The following undesirable effects considered related to treatment were reported during treatment with LUMIGAN™ 0.01 % eye drops. Most were ocular, mild and none was serious.
The frequency is defined as follows: Very Common (>= 1/10); Common (>=1/100 to <1/10); Uncommon (>=1/1,000 to <1/100); Rare (>= 1/10,000 to <1/1,000); Very Rare (< 1/10,000).
Eye disorders
Very Common:Ocular/Conjunctival hyperemia; Common: Eye irritation, Erythema of eyelid, Eye pruritus, Eyelids pruritus, Growth of eyelashes, Punctate keratitis;
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Common: Hypertrichosis, Skin hyperpigmentation;
General disorders and administration site conditions
Common: Instillation site irritation.
LUMIGAN™ 0.03%
On combining the 12-month data from 2 phase 3 monotherapy studies that compared once daily LUMIGAN™ 0.03% eye drops solution (multidose) with timolol, in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension, the most frequently reported, treatment-related, adverse events were: conjunctival hyperemia (mostly mild and thought to be of a non-inflammatory nature) in 45% of patients, growth of eyelashes (43%) and ocular pruritus (15%). Less than 9% of patients discontinued due to any adverse event. Extension studies up to 5 years did not indicate any side effects not already seen in the 12-month studies. The following undesirable effects were reported during monotherapy clinical trials with LUMIGAN™ 0.03% eye drops and considered by Allergan to be likely to be treatment related. Most were ocular, mild to moderate, and none was serious. Data are included from the LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD arms of the studies which had a Timolol control group giving a combined N of 739, LUMIGAN™ 0.03% patients and 504, Timolol.
The frequency is defined as follows: Very Common (>= 1/10); Common (>=1/100 to <1/10); Uncommon (>=1/1,000 to <1/100); Rare (>=1/10,000 to <1/1,000); Very Rare (<1/10,000).
Eye disorders
Very common: Conjunctival ocular hyperemia, growth of eyelashes, eye pruritus; Common: Allergic conjunctivitis, asthenopia, blepharitis, blepheral pigmentation, conjunctival edema, eye discharge, Eye irritation, Eye pain, Eyelash discoloration (darkening), Eyelid erythema, eyelid pruritus, foreign body sensation in eyes, increased iris pigmentation, lacrimation increased, ocular burning, ocular dryness, photophobia, punctate keratitis, visual disturbance/ blurred vision; Uncommon: iritis.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Common: Skin hyperpigmentation; Uncommon: Hirsutism.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03% multidose. Because postmarketing reporting is voluntary and from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate the frequency of these reactions:
LUMIGAN™ 0.01%
Eye disorders - Blepharal pigmentation, dry eye, eye discharge, eye edema, eyelid edema, Foreign body sensation in eyes, Iris hyperpigmentation, lacrimation increased, periorbital and lid changes including deepening of the eyelid, macular edema, eye pain, blurred vision.
Immune system disorders - hypersensitivity reaction including signs and symptoms of eye allergy and allergic dermatitis.
Nervous system disorders - headache.
Respiratory, thoracic disorders - asthma, exacerbation of asthma, dyspnea.
LUMIGAN™ 0.03%
Eye disorders - periorbital and lid changes including deepening of the eyelid sulcus erythema (periorbital), eyelid edema, macular edema.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders - hair growth abnormal.
Gastrointestinal disorders - nausea.
Immune system disorders - hypersensitivity reaction including signs and symptoms of eye allergy and allergic dermatitis.
Nervous system disorders - dizziness, headache.
Vascular disorders - hypertension.
Respiratory, thoracic - asthma, exacerbation of asthma, dyspnea.
7. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
7.1 Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03% (Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) administration in pregnant women. Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response LUMIGAN™ should be administered during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
7.2 Lactation
It is not known whether LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03% is excreted in human milk, although in animal studies, bimatoprost has been shown to be excreted in breast milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when LUMIGAN™ is administered to a nursing woman.
7.3 Pediatric Use
Use in pediatric patients has not been evaluated
and therefore use is not recommended in children or adolescents.
7.4 Geriatric Use
No overall clinical differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and other adult patients.
7.5 Renal Impairment
There are no data specific for this patient population and the product should therefore be used with caution in such patients.
7.6 Hepatic Impairment
LUMIGAN™ has not been studied in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment and should therefore be used with caution in such patients. In patients with a history of liver disease or abnormal ALT, AST and/or bilirubin at baseline, LUMIGAN™ 0.03% had no adverse effect on liver function over 48 months.
7.7 Compromised Respiratory Function
LUMIGAN™ has not been studied in patients with compromised respiratory function and should therefore be used with caution in such patients. In clinical studies, in those patients with a history of a compromised respiratory function, no significant untoward respiratory effects were seen.
7.8 Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
As with any ocular treatment, if transient blurred vision occurs at instillation, the patient should wait until the vision clears before driving or using machinery.
8. OVERDOSAGE
No information is available on overdosage in humans. If overdose with LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03% (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) occurs, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive.
If overdose occurs, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. If LUMIGAN™ is accidentally ingested, the following information may be useful: in 2-week oral rat and mouse studies, doses of bimatoprost up to 100 mg/kg/day did not produce any toxicity. This dose expressed as mg/m2 is at least 70-times higher than the accidental dose of one bottle of bimatoprost 0.03% eye drops solution in a 10 kg child.
9. DESCRIPTION
LUMIGAN™ 0.01 % and 0.03% (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) is a synthetic prostaglandin analog with ocular hypotensive activity. Its chemical name is (Z)-7- [(1R,2R,3R,5S)-3,5-Dihydroxy-2-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1-pentenyl] cyclopentyl]-5-N-ethylheptenamide, and its molecular weight is 415.58. Its molecular formula is C25H37NO4. Lumigan chemical structure is:

Bimatoprost is a powder, which is very soluble in ethyl alcohol and methyl alcohol and slightly soluble in water. LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03% is a clear, isotonic, colorless, sterile ophthalmic solution with an osmolality of approximately 290 mOsmol/kg.
LUMIGAN™ 0.01% contains Active: bimatoprost 0.1 mg/mL; Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.2 mg/mL; Inactives: sodium chloride; Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate, Citric acid monohydrate and purified water. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid may be added to adjust pH. The pH during its shelf life ranges from 6.8-7.8.
LUMIGAN™ 0.03% contains Active: bimatoprost 0.3 mg/mL; Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.05 mg/mL; Inactives: sodium chloride, Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate, Citric acid monohydrate and purified water. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid may be added to adjust pH.
10. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
10.1 Mechanism of Action
Bimatoprost is a synthetic prostamide, structurally related to prostaglandin F2a (PGF2a). Bimatoprost is a potent ocular hypotensive agent. Bimatoprost efficacy may be related to a dual mechanism of action on aqueous humour outflow that involves uveoscleral and trabecular meshwork Schlemm’s canal pathways. Studies in human models of the trabecular meshwork/Schlemm’s canal outflow pathways have demonstrated that bimatoprost produces marked increases in hydraulic conductivity that are prostamide receptor mediated.
10.2 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:
Bimatoprost penetrates the human cornea and sclera well in vitro. The mean corneal permeability coefficient was 3.24 x 10-6 cm/sec. Bimatoprost penetrated human scleral tissue better than corneal tissue with a mean scleral permeability coefficient of 14.5 x 10-6 cm/sec. After ocular administration, the systemic exposure of bimatoprost is very low with no accumulation over time. After once daily ocular administration of one drop of bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03% was administered once daily to both eyes of healthy subjects for two weeks, blood concentrations peaked within 10 minutes after dosing and declined to below the lower limit of detection (0.025 ng/mL) within 1.5 hours after dosing. Mean Cmas and AUC0-24hr values were similar on days 7 and 14 at approximately 0.08 ng/mL and 0.09 ng*hr/mL, respectively, indicating that a steady state was reached during the first week of ocular dosing.
The blood concentrations of bimatoprost from patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension in 2 Phase 3 safety and efficacy studies were measured (N=88 on once- daily treatment and N=89 on twice-daily treatment). The samples were collected at approximately 5 minutes after the evening dose on day 0 and at 3, 6 and 12 months. Bimatoprost blood concentrations were similar to those observed in normal, healthy subjects and there was no significant systemic drug accumulation over time.
Distribution:
Bimatoprost is moderately distributed into body tissues with a steady-state volume of distribution of 0.67 L/kg. In human blood, bimatoprost resides mainly in the plasma. Bimatoprost was approximately 88% bound to human plasma proteins at concentrations ranging from 1 to 250 ng/mL that was concentration independent. Up to 20% of bimatoprost was bound reversibly to synthetic melanin at concentrations ranging from 0.2-100 pg/mL which was also concentration independent
Metabolism:
Bimatoprost is not extensively metabolized in human eye and it is the major circulating species in the blood once it reaches the systemic circulation following ocular dosing. Bimatoprost then undergoes glucuronidation, hydroxylation, N-deethylation and deamidation to form a diverse variety of metabolites. The glucuronide conjugates of bimatoprost are the most abundant metabolite excreted in urine and faeces. There is evidence that hydrolysis of bimatoprost to the free acid is not a prerequisite for its ocular hypotensive activity.
The effects of bimatoprost treatment on hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes was investigated in rats and monkeys following one month of daily intravenous administration. Systemic drug exposures were at least 4,000 times greater than those seen in humans following QD ophthalmic administration. Bimatoprost was found to have no significant effect on any of the hepatic microsomal enzyme activities in cynomolgus monkeys. In female rats, an increase in the activity of UDP-glucuronyl transferase was observed. In the male rats, a marginal reduction in the rate of testosterone 16β-hydroxylation were the only findings. Neither of these observations is expected to have any clinically significant consequences in humans.
Elimination:
Following an intravenous dose of radiolabeled bimatoprost (3.12 mcg/kg) to six healthy subjects, the mean maximum blood concentration of total radioactivity was 14.5 ng/eq/mL. Total radioactivity was eliminated from the body with a short half-life of 1.74 hours. The blood concentration of intact bimatoprost was
12.2 ng/mL at maximum and declined rapidly with an elimination half-life of 0.771 hour (approximately 45 minutes). Blood concentrations of the acid metabolite, were much lower than those of bimatoprost as peak concentration was 0.12 ng/mL. The total blood clearance (Clb) of unchanged bimatoprost was 1.50 L/hr/kg.
Sixty-seven percent of the administered dose of bimatoprost was excreted in the urine with only a small fraction excreted as unchanged drug. Twenty-five percent of the dose was recovered in feces of which 15-40% was eliminated as unchanged drug.
To support the registration of 0.01% bimatoprost/200 ppm BAK ophthalmic solution, 4 pharmacokinetic studies were conducted to assess the ocular absorption of bimatoprost 0.01% using primary cultures of rabbit cornea epithelia in vitro (Study Report PK-04-168), and ocular absorption in New Zealand White (Study Report PK- 04-163) and Dutch Belted (Study Reports PK-06-108 and PK-07-086) rabbits in vivo.
Using both in vitro and in vivo methods, it was determined that increasing concentration of BAK in LUMIGAN™ enhanced ocular absorption of bimatoprost and lowered systemic exposure to bimatoprost.
Characteristics in Elderly Patients
There was no significant systemic accumulation of bimatoprost following twice-daily dosing for 7 days in either young (18-44 years, mean = 28.5) or elderly patients (65-80 years, mean = 71.0) (Study Reports 192024- 012 and PK-00-065). Bimatoprost appeared rapidly in the blood in both age groups, and was below the LLOQ by 1.5 hours in most patients. Systemic exposure was higher in the elderly than the young following both single and multiple dosing (124% and 213%, respectively). The mean AUC0-24hr value of 0.0634 ng*hr/mL in elderly subjects was statistically significantly higher than that of 0.0218 ng*hr/mL in young subjects, suggesting the existence of an age effect. However, this finding is not considered clinically relevant as bimatoprost exhibits similar efficacy and safety profiles in both the young and elderly populations.
11. PRECLINICAL SAFETY DATA11.1 Acute and Chronic Toxicity Studies
Effects in non-clinical studies were observed only at exposures considered sufficiently in excess of the maximum human exposure indicating little relevance to clinical use.
The toxicity of bimatoprost has been assessed in ocular instillation studies up to 1 month duration in New Zealand White (NZW) rabbits up to 6 months duration in Dutch belted (DB) rabbits and up to 1 month duration in dogs.
Slight, transient ocular discomfort and conjunctival hyperemia were noted in NZW rabbits in both the 3-day and the 1-month studies at concentrations as low as 0.001%. However, rabbits administered placebo solutions exhibited the same response. Dogs exhibited ocular discomfort and transient slight conjunctival erythema at concentrations as low as 0.001%, and in placebo controls. Administration of bimatoprost or placebo to DB rabbits did not cause ocular sensitivity in any study. Since ocular sensitivity was observed in NZW rabbits and dogs QID, but not in DB rabbits given the same formulation of bimatoprost and placebo BID, these effects may be due to the higher frequency of dosing. No systemic effects were noted in the 6-month ocular rabbit study which achieved a maximal AUC that was approximately 53-fold higher than the human value resulting from the intended bimatoprost clinical regimen.
No treatment-related systemic effects were observed in cynomolgus monkeys when 0.03% or 0.1% bimatoprost ophthalmic formulation was instilled to the eye once or twice daily for 1 year. An increase in iris pigmentation was noted in some animals in all treated groups. No associated increase in melanocyte number was observed with the pigmentation. It appears that the mechanism of increased iris pigmentation is due to increased stimulation of melanin production in melanocytes and not to an increase in melanocyte number.
No treatment-related systemic effects were observed in cynomolgus monkeys administered from 0.01 to 1.0 mg/kg/day bimatoprost intravenously for 17 weeks. The increase in iris pigmentation observed at 13 weeks in the ocular study was not observed at 17 weeks in the IV study. This finding suggests that the local effects are important and may be related to the mean residence time of the solution in the eye.
Monkeys administered 1 drop of bimatoprost 0.03% QD of BID or bimatoprost 0.1% BID for 52 weeks exhibited a dose-related increase in the prominence of the periocular sulci, resulting in a widening of the palpebral fissure of the treated eye. The severity and incidence of this effect was temporally related to dose. No functional or microscopic change related to the periocular change was observed. The highest dose (0.1% twice daily) produced at least 65 times the systemic drug exposure seen in humans treated with 1 drop into each eye of 0.03% bimatoprost once daily for 2 weeks.
This effect was also observed with IV administration of 0.01 mg/kg/day in monkeys for 17 weeks. IV administration of 0.01 mg/kg/day produced an AUCde of 235-fold greater than that of humans given 0.03% ocularly QD. In both studies the periocular effects were resolved following cessation of treatment. No functional or anatomic abnormalities of the eye were detected. The underlying cause of the prominence of the sulci and widening of the palpebral fissures observed with ocular and IV administration in monkeys is unknown. Since periocular changes were observed with both ocular and IV administration of bimatoprost, these studies suggest there are local receptor-specific effects underlying the periocular effects in monkeys. Since periocular effects occurred at exposures ranging from 8- to 235-fold greater than those in humans given the maximum Intended clinical regimen the risk to humans is low.
No effects were observed in mice given 4 mg/kg/day bimatoprost orally for 3 months. This dose achieved systemic exposure that was at least 149 times higher than that observed in humans treated with the intended clinical regimen. Female mice given oral doses of 8 mg/kg/day showed a reversible thymic lymphoid proliferation. This observation was only made in mice and at a dose far exceeding the intended human exposure (460-fold higher).
A decrease in food consumption and an increase in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were observed in male rats given >= 8 mg/kg/day for 13 weeks. Reversible decreases in body weight and body weight gain were observed in both genders at >= 4 mg/kg/day. A reversible increase in ovarian weight accompanied by delayed regression of corpora lutea was noted in females>= 4 mg/kg/day. The ovarian effects were observed only in studies with nulliparous rats and since these effects were not seen in other species or pregnant rats suggesting that bimatoprost may uniquely affect the luteal cycle in nulliparous rats. The species specificity and considerable exposure margins indicate that risk of ovarian effects is negligible in humans. There were no drug related effects in either gender at 0.1 mg/kg/day. A slight decrease (9%) in body weight in females (2 mg/kg/day) versus control was observed in the 1-year study in rats. There was a slight increase in transaminase activity (approximately 3-fold) in males of all dose groups but these changes were not associated with any histopathological lesions and reversibility was apparent. Ovarian and hepatic effects were reversible, and considered species specific since these changes had not been observed in mice and monkeys at systemic exposures up to 2800 to 14000-fold higher, respectively, than those occurring in humans given ocular doses of bimatoprost 0.03%.
The systemic exposure after dermal application of bimatoprost 0.03% on the upper eyelid margin is not expected to exceed that obtained after ocular dosing in humans.
A 1-month toxicity study in female NZW rabbits was performed to support registration of 0.01% bimatoprost/200 ppm BAK ophthalmic solution. Mild conjunctival hyperemia and mild corneal degeneration and regeneration were observed with all formulations (including placebo vehicle) containing 200 ppm BAK and 0%, 0.015% or 0.02% bimatoprost.
In a 6-month ocular toxicity study in male and female DB rabbits there were no indications of general or ocular toxicity related to ocular dosing of either 0.01 % bimatoprost/200 ppm BAK ophthalmic solution or 0.0125% bimatoprost/200 ppm BAK ophthalmic solution, when administered up to three times daily over a 6-month period to DB rabbits. Overall, these data support the safety of 0.01 % bimatoprost/200 ppm BAK ophthalmic solution.
Mutagenicity
Bimatoprost was not mutagenic or clastogenic in the Ames test, in the mouse lymphoma test, or in the in vivo mouse micronucleus tests.
Carcinogenicity
Bimatoprost was not carcinogenic in either mice or rats when administered by oral gavage at doses up to 2 mg/kg/day and 1 mg/kg/day respectively (approximately 192 and 291 times the maximum recommended human exposure based on blood AUC levels after topical ophthalmic administration, respectively) for 104 weeks
Impairment of Fertility
No impairment of fertility occurred in rats when males were treated for 70 days prior to cohabitation and females were treated for 15 days prior to mating. Treatment was continued in males until copulation was observed and in females through gestation day 7. The highest dose (0.6 mg/kg/day) achieved systemic exposure that was 103 times that observed in humans treated with 1 drop of 0.03% bimatoprost in each eye once daily for 2 weeks.
Teratogenicity
Bimatoprost given orally at doses up to 0.3 or 0.6 mg/kg/day to pregnant rats during gestation day 6 through 17 caused abortion but no drug-related developmental effects. This effect was also seen in mice receiving 0.3 mg/kg/day during gestation day 6 through 15. The maternal no-observable-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) of bimatoprost was 0.1 or 0.3 mg/kg/day for mice or rats, respectively. Abortion was expected as a rodent-specific pharmacological effect. The lowest effect dose of 0.3 or 0.6 mg/kg in mice and rats, respectively, achieved systemic exposure (AUC) that was at least 33 or 103 times higher respectively, than that observed in humans treated with the intended clinical regimen (following topical ophthalmic administration of 0.03% bimatoprost).
Treatment of F0 female rats given 0.3 mg/kg/day (at systemic exposure estimated 41 times the intended clinical dose) or greater caused maternal toxicity as evidenced by reduced gestation length, increased late resorption, fetal death, and postnatal mortality and reduced pup body weight (a rodent-specific pharmacological effect). No effects on postnatal development and mating performance of the F1, offspring were observed in groups treated with dosages as high as 0.1 mg/kg/day. Neurobehavioral function, caesarean-sectioning parameters, and litter parameters in F1, rats were unaffected by doses as high as 0.3 mg/kg/day.
12. CLINICAL EFFICACY
LUMIGAN™ 0.01% (Multidose)
In a double-masked, paired-eye, 5-day Phase 2 study in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension LUMIGAN™ was compared with bimatoprost in concentrations ranging from 0.01% to 0.02% in a new formulation that contained 200 ppm BAK (LUMIGAN™ 0.03% multidose contains 50 ppm BAK). The objective of this study was to determine if the test formulations could achieve the same IOP control while reducing ocular adverse events compared with LUMIGAN™. In this study, bimatoprost 0.01% (200 ppm BAK) showed no clinically relevant differences in IOР-lowering and improved ocular safety/tolerability compared with LUMIGAN™ and this concentration was chosen for further evaluation.
In a 12-month pivotal study LUMIGAN™ 0.01 % eyedrops, solution, once daily, (Bimatoprost 0.01%) was shown to be an effective intraocular pressure lowering therapy. Bimatoprost 0.01 % was non-inferior to LUMIGAN™ the upper limit of the CIS (95% or 97.5% according to the Hochberg procedure) of the between-treatment difference in mean IOP was within the 1.50 mm Hg margin at all (17/17) timepoints. Both treatments showed statistically and clinically significant mean decreases from baseline IOP at all follow-up timepoints (p < 0.001). Mean changes from baseline IOP ranged from -5.2 to -7.8 mm Hg for bimatoprost 0.01%, and -5.6 to -8.0 mm Hg for LUMIGAN™ At any visit, the diurnal IOP values for Bimatoprost 0.01%, measured over the 12-month study period, differed by no more than 1.1 mmHg throughout the day and were never greater than 17.9 mmHg.
In a 1 -month, vehicle-controlled, parallel group study of the safety and efficacy of bimatoprost 0.01% ophthalmic solution once-daily (QD) in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension whose intraocular pressure was previously controlled with latanoprost 0.005%, bimatoprost 0.01% significantly reduced IOP from the latanoprost-treated baseline and this change was superior to vehicle at all timepoints. Furthermore, the between- group difference in mean peak change in macroscopic hyperemia from a latanoprost- treated baseline was less than 0.5 grade, meeting the pre-specified non-inferiority criterion, and thus, bimatoprost 0.01 % was not inferior to vehicle The safety profile indicates that both treatments were well tolerated.
LUMIGAN™ 0.03% (Multidose)
Phase 3 Monotherapy Studies
In two 12-month, phase 3 studies, the safety and efficacy of LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD, evening dosing, as a monotherapy treatment for elevated IOP were compared with LUMIGAN™ 0.03% BID and timolol 0.5% BID dosing in 1,198 total patients with glaucoma or OHT. Since the 2 studies were identical in design, their data were pooled for analysis (Higginbotham et al, 2002). LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD was superior to LUMIGAN™ 0.03% BID and timolol BID in lowering elevated IOP at each follow-up visit for hours 0, 2 and 8 for the entire 12-month study duration. The mean change from baseline in morning (08:00) intraocular pressure ranged from - 7.9 to -8.8 mmHg for patients on QD LUMIGAN™ 0.03%. At any visit, the mean diurnal IOP values measured over the12-month study period differed by no more than 1.3 mmHg throughout the day and were never greater than 18.0 mmHg.
Extension of the Phase 3 Monotherapy Trials
Patients from selected sites from the phase 3 trials were entered into an extension study that was conducted for up to 4 years. A total of 379 patients entered the extension phase. At the end of 2 years of treatment LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD was superior to LUMIGAN™ 0.03% BID and timolol in IOР-lowering efficacy at each follow-up visit for all time points.
At the month 24 visit, patients in the LUMIGAN™ 0.03% BID group were switched, in a masked fashion, to LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD therapy, and are referred to as the BID/QD group. Patients who were originally randomized to LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD group or timolol BID group remained randomized to their respective therapies/original treatment regimens. At the end of 3 years, LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD showed superior efficacy to timolol at all follow-up timepoints. In addition, there were no statistically significant differences in mean change from baseline IOP at Hour 0, at any follow-up visit, between the patients who had received LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD throughout and those switched from LUMIGAN™ 0.03% BID to QD.
At the end of 4 years LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD treatment
showed superior efficacy to timolol BID.
In a 6-month, phase 3b, clinical study of LUMIGAN™ 0.03% eye drops solution versus latanoprost, a statistically superior reduction in morning mean IOP (ranging from -7.6 to -8.2 mmHg for bimatoprost versus -6.0 to -7.2 mmHg for latanoprost) was observed at all visits throughout the study. Furthermore, at all follow-up timepoints, mean IOP values were significantly lower with bimatoprost than with latanoprost
Phase 3 Adjunctive Therapy Studies
In a 12-week, phase 3 study, the safety and efficacy of LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD (evening) was compared with latanoprost 0.005% QD (evening), each as an adjunctive treatment with a beta-blocker, in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension who were inadequately controlled on beta-blocker therapy alone.
As an adjunctive treatment to topical beta-blocker therapy, LUMIGAN™ 0.03% administered QD was as effective as latanoprost 0.005% administered QD in lowering the elevated IOP. At month 3, mean diurnal IOP at hours 0, 2, and 8 ranged from 16.14 to 17.07 mm Hg with LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD and 16.92 to 17.82 mm Hg with latanoprost QD each administered adjunctively with a topical beta-blocker (BID), for 3 months.
A 12-month, phase-3 study of LUMIGAN™ 0.03% as an adjunctive treatment of elevated IOP was completed. This was a multicenter, double-masked, randomized, vehicle-controlled, parallel study in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension who were uncontrolled on beta-blocker therapy alone. The purpose of the study was to compare the safety and efficacy of LUMIGAN™ 0.03% ophthalmic solution administered QD with LUMIGAN™ 0.03% ophthalmic solution administered BID and with vehicle ophthalmic solution administered BID, each administered adjunctively with a topical beta-blocker (BID), for 3 months. In order to provide additional long-term safety and efficacy data, masked treatment with LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD and BID, adjunctively with a topical beta-blocker administered BID, continued for an additional 9 months. Those patients previously receiving vehicle treatment were randomized to one of the 2 active treatment arms in a masked manner for the 9 months extension.
The results demonstrated that both LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD/beta-blocker and LUMIGAN™ 0.03% BID/beta- blocker were superior to vehicle BID/beta-blocker in lowering the elevated IOP of patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension inadequately controlled on beta blocker alone. However, superiority of LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD/beta-blocker compared with LUMIGAN™ 0.03% BID/ beta-blocker in change from baseline was seen at isolated timepoints, particularly at Hour 8. Also, the lOP-lowering effect of LUMIGAN™ 0.03% QD adjunctively with a topical beta-blocker was maintained over the entire 1 -year study duration.
Lumigan™ 0.01% & 0.03%
Limited experience is available with the use in patients with open-angle glaucoma with pseudoexfoliative and pigmentary glaucoma, and chronic angle-closure glaucoma with patent iridotomy.
No clinically relevant, treatment-related, effects on heart rate and blood pressure have been observed in clinical trials.
In patients enrolled in the long-term LUMIGAN™ 0.03% studies who had a history of liver disease or abnormal ALT, AST and/or bilirubin at baseline, LUMIGAN™ 0.03% had no adverse effect on liver function over 48 months. With regard to liver function tests, review of the overall clinical trial data for LUMIGAN™ 0.03% showed that the vast majority of patients' values remained relatively unchanged in all treatment groups during the study period. Where there appeared to be clinically relevant worsening, it was possible to document a medical history or a concomitant medication which could at least possibly explain the abnormality. This suggests that patients with prior hepatic dysfunction are not at increased risk of worsening of established disease.
13. HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LUMIGAN™ (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.01% is supplied sterile in opaque white low density polyethylene plastic bottles with dropper tips and high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps in the following sizes: 3 mL fill in a 5 mL container.
LUMIGAN™ (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.03% is supplied sterile in opaque white low density polyethylene plastic bottles with dropper tips and high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps in the following sizes: 3 mL fill in 5 mL container.
Storage: LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03% should be stored at 2° to 25°C (36° to 77°F).
14. PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
14.1 Potential for Pigmentation
Patients should be advised about the potential for increased brown pigmentation of the iris, which may be permanent. Patients should also be informed about the possibility of eyelid skin darkening, which may be reversible after discontinuation of LUMIGAN™ 0.01 % and 0.03% (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution).
14.2 Potential for Eyelash Changes
Patients should also be informed of the possibility of eyelash and vellus hair changes in the treated eye during treatment with LUMIGAN™ 0.01% and 0.03%. These changes may result in a disparity between eyes in length, thickness, pigmentation, number of eyelashes or vellus hairs, and/or direction of eyelash growth. Eyelash changes are usually reversible upon discontinuation of treatment.
14.3 Handling the Container
Patients should be instructed to avoid allowing the tip of the dispensing container to contact the eye, surrounding structures, fingers, or any other surface in order to avoid contamination of the solution by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions.
14.4 When to Seek Physician Advice
Patients should also be advised that if they develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), have ocular surgery, or develop any ocular reactions, particularly conjunctivitis and eyelid reactions, they should immediately seek their physician's advice concerning the continued use of LUMIGAN™ 0.01 % and 0.03%.
14.5 Use with Contact Lenses
Patients should be advised that LUMIGAN™ 0.01 % and 0.03% contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride, which may be absorbed by and cause discoloration of soft contact lenses. Patients wearing soft (hydrophilic) contact lenses should be instructed to remove contact lenses prior to administration of LUMIGAN™ (multidose) and wait at least 15 minutes following administration before reinserting soft contact lenses.
14.6 Use with Other Ophthalmic Drugs
Patients should be advised that if more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five (5) minutes between applications.
LUMIGAN™ 0.01% Manufactured by:
Allergan Pharamceuticals Ireland
Castlebar Road, Westport, Co. Mayo, Ireland
LUMIGAN™ 0.03% Manufactured by:
Allergan Sales LLC
8301, Mars Drive, Waco, Texas, 76712, U.S.A.
Imported & Marketed by:
Allergan India Pvt. Ltd.; Bangalore
© 2017 Allergan. All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.